Indexing & Abstracting
Full Text
Research ArticleDOI Number : 10.36811/ijpsh.2021.110031Article Views : 67Article Downloads : 48
Economic losses caused by rodents in some types of maize fields at Farshout District, Qena Governorate, Egypt
Ahmed AA Elrawy1, Nashaat A Mahmoud1, Saudi AS Baghdadi1, Abd El-Aleem SS Desoky2*
1Agric. Zoology and Nematology Dept., Faculty of Agric., Al-Azhar University, Assiut, Egypt
2Plant Protection Department, Faculty of Agriculture Sohag University, Egypt
*Corresponding Author: Abd El-Aleem Saad Soliman Desoky, Plant Protection Department, Faculty of Agriculture Sohag University, Egypt, Email: abdelalem2011@gmail.com
Article Information
Aritcle Type: Research Article
Citation: Ahmed AA Elrawy, Nashaat A Mahmoud, Saudi AS Baghdadi, et al. 2021. Economic losses caused by rodents in some types of maize fields at Farshout District, Qena Governorate, Egypt. Int J Plant Sci Hor. 3: 53-57.
Copyright: This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited. Copyright © 2021; Ahmed AA Elrawy
Publication history:
Received date: 09 July, 2021Accepted date: 15 July, 2021
Published date: 17 July, 2021
Abstract
This study was conducted to estimate the quantitative damage caused by rodent infestation to some types of maize and its financial transfer, at Al-Dahsa village in Farshout district, Qena Governorate, Egypt, during study period 2018/2019. The percentage of the quantitative and economic losses in maize varieties caused by rodents show that the highest value of loss was recorded in genotype single cross (HYTECH 2066) were about (3.91 and 3.00 Ardab/ feddan with a value of about (2737 and 2100 pounds), followed by the (Balady) type with about (3.90 and 2.34 Ardab/fed) with a value of about (2730 and 1638 pounds), followed by the single hybrid genotype (HYTECH 2055) about (3.26 and 2.57 Ardab/fed) with a value of about (2282 and 1799 pounds), while the moderate loss was recorded in crossbreeding Triple genetic (National seeds 11 "National seeds company") about (2.40 and 2.10 Ardab/fed) with a value of about (1608 and 1407 pounds), followed by the three-way genotype (National seeds 310) with about (2.30 and 1.84 Ardab/fed) with a value of about (1541 and 1233) pounds, while the lowest value was recorded in the individual genotype (National seeds 6) with about (1.30 and 1.04 Ardab/fed) with a value of about (871 and 697 pounds), followed by the individual hybrid genotype (National seeds 4), about (1.50 and 1.20 Ardab/fed) with a value of about (1005 and 804 pounds). The study indicates the interest in agricultural operations, taking preventive measures and implementing appropriate control programs for the maize varieties most infested with rodents.
Keywords: Rodent Infestation; Financial Transfer; Type of Maize; Ardab; Feddan
Introduction
Maize (Zea mays L) is the third most cereal crop in the world, providing nutrient of humans and animals. The behavior of rodents can vary widely from place to place. Maize crop fields recorded as suitable host to rodent pests by many workers in the world [1-8]. Rodents are considered one of the most important pests in Egypt. They cause great economic losses to farmers (destroying agricultural crops and stored products [9]. The study aims to know the material losses resulting from the infestation of rodents for the most important types of maize.
Materials and Methods
This study was conducted over two consecutive years (2018 and 2019). The field experiment was conducted in Al-Dahsa village, Farshout District, Qena Governorate-Egypt. The damage caused by rodents was evaluated for the most important varieties of maize, namely HYTECH 2066, Balady, HYTECH 2055, National seeds 11, National seeds 310, National seeds 6 and National seeds 4. Damage to rodent species was monitored in the field, based on the frequency of encountering corn cob damage until harvest time. The direct counting method was used in order to determine the damages of rodents. Thirty plants were randomly sampled from the field of each replicate and crop damage was measured. Half feddan each treatment of maize during two successive years was chosen to this experiment. Samples from each experiment were 30 plants representing five randomized replicates. The degree of damage due to rodent species in the ears was estimated according to [10] by using the following equations:
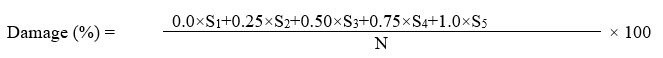
Were:
S1= No of undamaged corn cob; S2= No. of 1/4 damaged corn cob; S3= No. of 1/2 damaged corn cob; S4= No. of 3/4 damaged corn cob; S5= No. of complete damaged corn cob; N= Total Number of investigated corn cob. The losses caused by the rodents were calculated for each training/feds and then transferred financially.
Results and Discussion
Data presented in (Tables 1 and 2) (Figures 1 and 2) showed that, the value of loss (quantitative) in cultivars of maize at two successive years at Qena Governorate. The percentage of economic losses caused by rodents show that the highest value of loss was recorded in genotype single cross (HYTECH 2066) was about (3.91and 3.00 Ardab/fed) worth about (2737 and 2100 pounds), representing about (17.00 and 15.17%) of the total production as a result of rodents attack in the case of cultivation alone, followed by Balady was about (3.90and 2.34 Ardab/fed) worth about (2730 and 1638 pounds), representing about (20.50 and 19.50%) of the total production as a result of rodents attack in the case of cultivation alone, followed by genotype single cross (HYTECH 2055) was about (3.26 and 2.57 Ardab/fed) worth about (2282 and 1799 pounds), representing about (14.83 and 13.50%) of the total production as a result of rodents attack in the case of cultivation alone at the first and second years respectively.
While the moderate value of loss was recorded in the genotype three way cross (National seeds 11) was about (2.40 and 2.10 Ardab/fed) worth about (1608 and 1407 pounds), representing about (11.50 and 11.00%) of the total production as a result of rodents attack in the case of cultivation alone, followed by genotype three way cross (National seeds 310) was about (2.30 and 1.84 Ardab/fed) worth about (1541 and 1233 pounds), representing about (10.83 and 9.67%) of the total production as a result of rodents attack in the case of cultivation alone at the first and second years respectively. While the least value of loss was recorded in the genotype single cross(National seeds 6) was about (1.30 and 1.04 Ardab/fed) worth about (871 and 697 pounds), representing about (4.83 and 4.50%) of the total production as a result of rodents attack in the case of cultivation alone, followed by genotype single cross (National seeds 4) was about (1.50 and 1.20 Ardab/fed) worth about (1005 and 804 pounds), representing about (6.17 and 6.00%) of the total production as a result of rodents attack in the case of cultivation alone at the first and second years respectively. The results similar with [7] found the losses to maize crop by large jird Meriones shawi (Thomas) were about 2 Ardab/fed and decreased to 0.9 Ardab/fed., At El-Behria Governorate, during 2001 and 2002 agriculture seasons, respectively. This study informs the future interest in the prevention of corn varieties most infested with rodents and the work of an integrated control program to reduce or prevent rodent infestation.
|
Table 1: Average percentage of economic losses caused by rodents in some types of maize at Qena Governorate (2018). |
||||||
|
Damage/ Egypt pounds |
Ave. Ardab/ price/ EGP |
Damage/ Ardab |
Damage % |
Ave. fadden yield/ Ardab |
Maize types |
No. |
|
2730 |
700 |
3.90 |
20.50 |
19 |
Balady |
1 |
|
2282 |
700 |
3.26 |
14.83 |
22 |
HYTECH 2055 |
2 |
|
2737 |
700 |
3.91 |
17.00 |
23 |
HYTECH 2066 |
3 |
|
1608 |
670 |
2.40 |
11.50 |
21 |
National seeds 11 |
4 |
|
1541 |
670 |
2.30 |
10.83 |
21 |
National seeds 310 |
5 |
|
1005 |
670 |
1.5 |
6.17 |
24 |
National seeds 4 |
6 |
|
871 |
670 |
1.3 |
4.83 |
27 |
National seeds 6 |
7 |
|
1824.86 |
682.86 |
2.65 |
12.24 |
22.43 |
Mean |
|
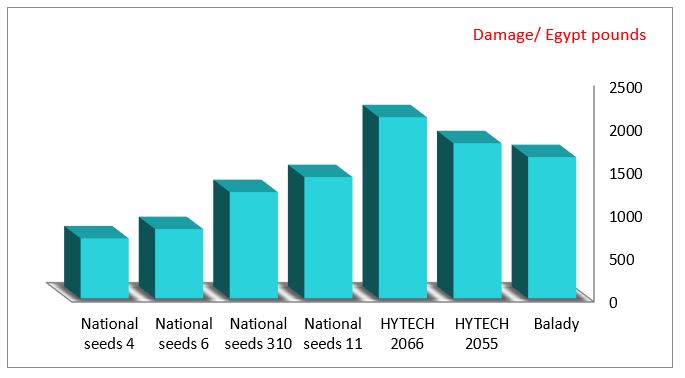
Figure 1: Average percentage of economic losses caused by rodents in some types of maize at Qena Governorate (2018).
|
Table 2: Average percentage of economic losses caused by rodents in some types of maize at Qena Governorate (2019). |
||||||
|
Damage/ Egypt pounds |
Ave. Ardab price/ EGP |
Damage/ Ardab |
Damage % |
Ave. fadden yield/ Ardab |
Maize types |
No. |
|
1638 |
700 |
2.34 |
19.50 |
12 |
Balady |
1 |
|
1799 |
700 |
2.57 |
13.50 |
19 |
HYTECH 2055 |
2 |
|
2100 |
700 |
3 |
15.17 |
20 |
HYTECH 2066 |
3 |
|
1407 |
670 |
2.10 |
11.00 |
19 |
National seeds 11 |
4 |
|
1233 |
670 |
1.84 |
9.67 |
19 |
National seeds 310 |
5 |
|
804 |
670 |
1.20 |
6.00 |
20 |
National seeds 4 |
6 |
|
697 |
670 |
1.04 |
4.50 |
23 |
National seeds 6 |
7 |
|
1382.57 |
682.86 |
2.01 |
11.33 |
18.86 |
Mean |
|
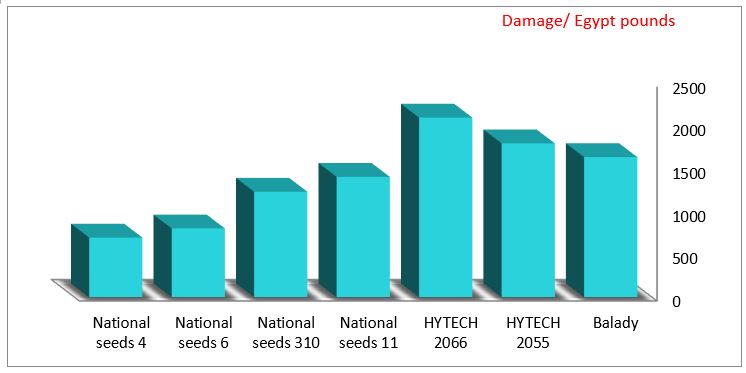
Figure 2: Average percentage of economic losses caused by rodents in some types of maize at Qena Governorate (2019).
References
1. Clark WR, Young RE. 1986. Crop damage by small mammals in no-till corn fields. J of Soil and water Conservation. 41: 338-341.
2. Keshta TMS. 1996. Studies on the house mouse Mus musculus L. M.Sc. Thesis, Fac. Agric, Al-Azhar Univ. Cairo. 164.
3. Abdel-Gawad KH, Farghal AI, El-Eraky SA. 2000. Damage caused by rodents to some field crops and date palm. The 2nd Sci Conf of Agric Sci Assiut.
4. Mulungu LS, Rhodes HM, Apia WM. 2005. Spatial patterns and distribution of damage in maize fields due to mastomys natalensis in Tanzania. Belg J Zool. 135: 183-185.
5. Ahmed HSK. 2006. Studies on damage caused by rodents on some field crops and its control in Upper Egypt (Assiut area). M.Sc. Thesis Agric. Al-Azhar Univ. 109.
6. El-Saady Maha A. 2009. Studies on rodents and its integrated control in Minia region. Ph.D. Thesis, Fac. Agric. Minia Univ. Minia. 160.
7. Metwally AM, Montasser SA, Al-Gendy AAR. 2009. Survey of rodent species and damage assessment caused by Meriones shawi isis (Thomas) in some field crops at Bustan Area. J App Sci Research. 5: 40-45.
8. Baghdadi SAS. 2012. Using of some environmentally available alternatives as rodenticides in Assiut area. Ph.D. Fac Agric. Al Azhar Univ. 149.
9. Desoky ASS. 2018. Rodent Damage in Maize Fields and their Control, Acta Scientific Agriculture. 2: 53-54.
10. Hamelink J. 1981. Assessing rat damage and yield losses in sugar cane, rice and maize. Book of rodent pests and their control. GTZ. AI-III B/5.




















